
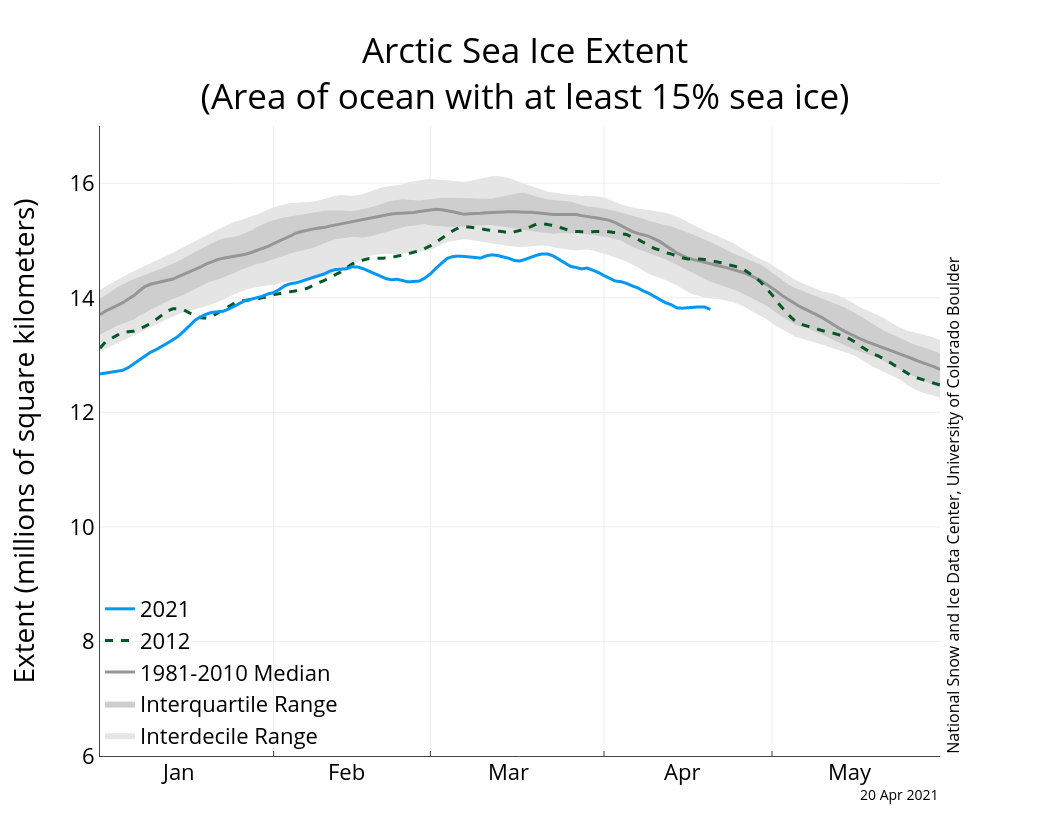
Based on satellite imagery, the Arctic sea ice reached its maximum extent for the year in March. According to the National Snow & Ice Data Center, this year’s maximum of 5.65 million square miles was the 9th lowest since reporting began 43 years ago. This number is 305,000 square miles below the 1981-2010 average. While the Arctic sea ice has been decreasing year after year, this year’s maximum was still 135,000 miles above the record minimum, which was set in 2017. While this year wasn’t the worst year on record, it is clear that things are getting worse, and scientists are estimating that if current trends continue, all of the Arctic sea ice could be gone by 2035.
What does this mean for California? Arctic sea ice plays a vital role in reflecting the sun’s energy back into space. With less sea ice present in the Arctic, seawater absorbs more of the sun’s incoming heat. This causes the ocean to warm, leading to more rain and less snow in the Sierras. Beyond blanketing our slopes in the snow that allows us to enjoy our favorite snow sliding activities, the Sierra snowpack plays many other crucial roles as well. According to the California Department of Water Resources, the Sierra snowpack provides California with 30% of its water. As this snowpack diminishes, California’s drought will worsen, leading to less water for agriculture, more wildfires, etc.
While the Arctic sea ice situation is currently quite bleak, we must continue our efforts to prevent as much sea ice loss as possible. On top of finding ways to decrease our greenhouse gas emissions, scientists and engineers are working towards other solutions as well. One of the most popular solutions currently on the table is strategically covering vital parts of the Arctic sea ice in silica beads. These beads, like sea ice, will reflect the sun’s energy back into space. Leslie Field, one of the lead scientists on this project, claims that this solution is safe because silica is already abundant in nature and is frequently flushed through ecosystems as rocks erode. Still, many scientists are wary of the long-term impacts this solution could have on the Arctic ecosystem. While this might not be the best solution, it is relieving to know that significant efforts are being put into the fight to save the Arctic sea ice.

Californians think they are the center of the world.