
This article was originally published on noaa.gov
NOAA issued its U.S. Spring Outlook today and for the second year in a row, forecasters predict prolonged, persistent drought in the West where below-average precipitation is most likely. NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center — part of the National Weather Service — is also forecasting above-average temperatures for most of the U.S. from the Desert Southwest to the East Coast and north through the Midwest to the Canadian border from April to June.
“NOAA’s Spring Outlook helps build a more weather and climate ready nation by informing local decision makers and emergency managers of this spring’s hazardous weather, such as extreme drought,” said NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad, Ph.D. “NOAA’s seasonal outlooks provide advanced warning of the conditions to come, enabling communities to make preparations that boost their resilience to these hazards.”
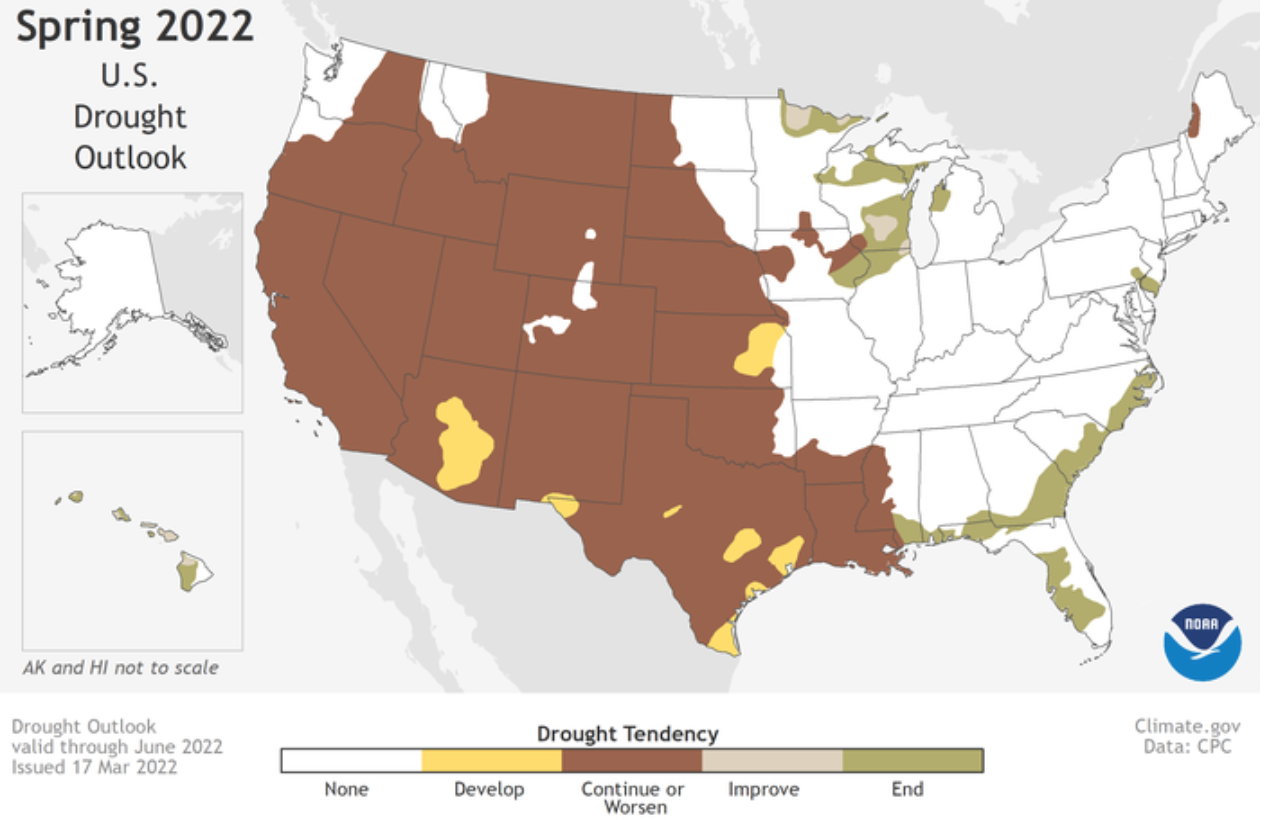
“Severe to exceptional drought has persisted in some areas of the West since the summer of 2020 and drought has expanded to the southern Plains and Lower Mississippi Valley,” said Jon Gottschalck, chief, Operational Prediction Branch, NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center. “With nearly 60% of the continental U.S. experiencing minor to exceptional drought conditions, this is the largest drought coverage we’ve seen in the U.S. since 2013.”
Short-term drought recently developed in a region stretching from North Carolina southward through parts of Florida. Dry conditions will bring an elevated risk of wildfires across the Southwest and southern Plains and north to the Central Plains, especially when high winds are present. Drought conditions in the Southwest are unlikely to improve until the late summer monsoon rainfall begins.
More than half of the U.S. is predicted to experience above-average temperatures this spring, with the greatest chances in the Southern Rockies and Southern Plains. Below-average temperatures are most likely in the Pacific Northwest and southeast Alaska.
Above-average precipitation is most likely in portions of the Great Lakes, Ohio Valley, mid-Atlantic and the west coast of Alaska, while below-average precipitation is forecast for portions of the Central Great Basin, Southwest, Central and Southern Rockies and Central and Southern Plains, eastward to the Central Gulf Coast.
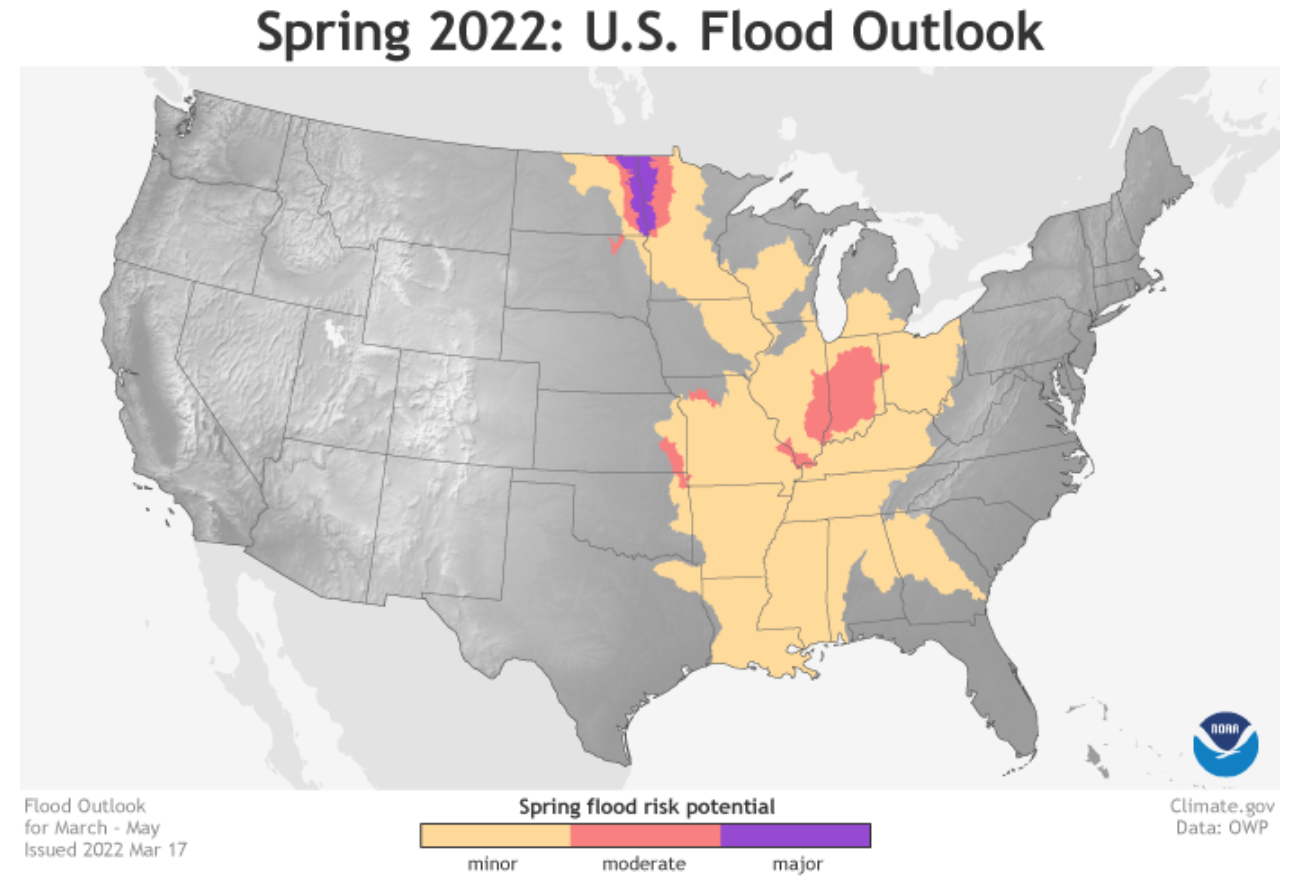
Spring flood risk
There is a minor-to-moderate flood risk throughout much of the eastern half of continental U.S., including the Southeast, Tennessee Valley, lower Mississippi Valley, Ohio Valley, and portions of the Great Lakes, upper Mississippi Valley, and middle Mississippi Valley. An above-normal ice breakup and flood potential is also present in Alaska.
“Due to late fall and winter precipitation, which saturated soils and increased streamflows, major flood risk potential is expected for the Red River of the North in North Dakota and moderate flood potential for the James River in South Dakota,” said Ed Clark, director, NOAA’s National Water Center.
Spring snowmelt in the western U.S. is unlikely to cause flooding.
NOAA’s National Hydrologic Assessment evaluates a number of factors, including current conditions of snowpack, drought, soil saturation levels, frost depth, streamflow and precipitation.