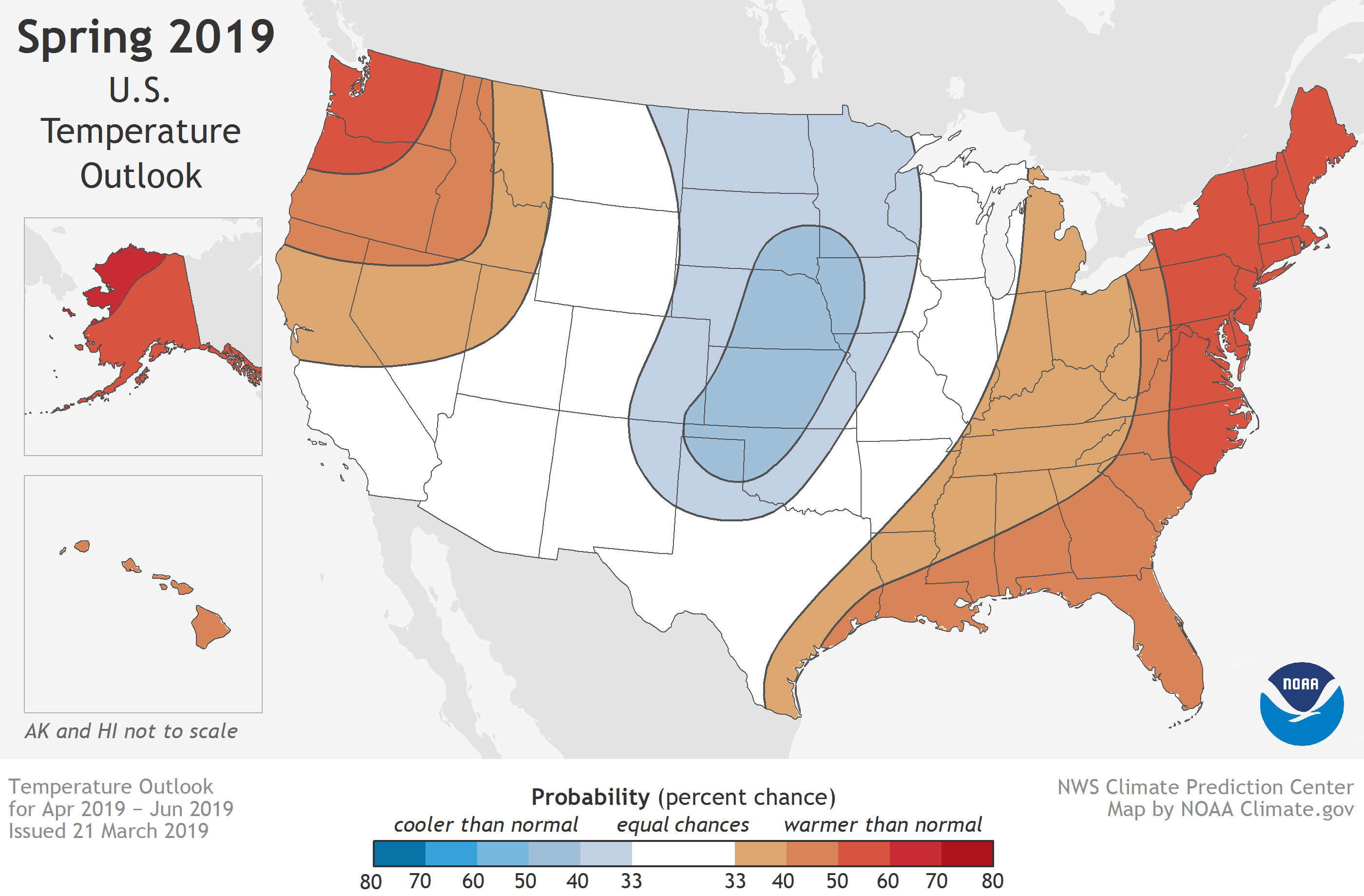
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center recently issued their new 90-day spring outlook, covering April, May, and June. Below-average temperatures are most likely in the Central and Southern Plains, where the saturated ground will slow down the seasonal warm up. Odds for a much warmer than average spring are likely in areas east of the Mississippi, and in the West and Pacific Northwest.
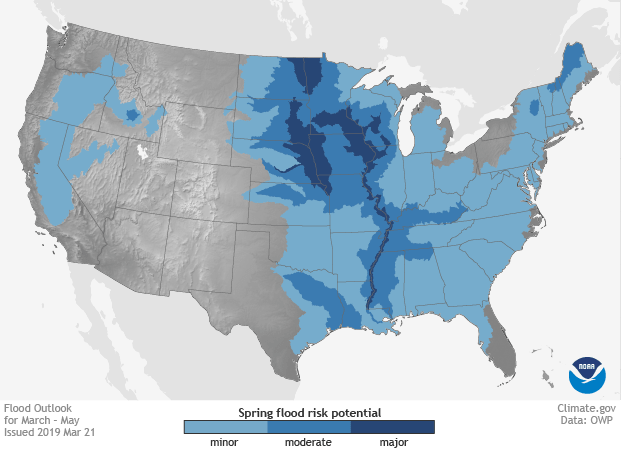
According to NOAA’s spring outlook for flood and climate, a wet winter has primed much of the Great Plains for spring flooding in 2019, with major flooding likely along the Red River of the North, the Missouri, and the Mississippi Rivers. Moderate flood risk extends upstream of those rivers to their tributaries, including the lower Ohio, the Cumberland, and Tennessee Rivers. Minor flood risk covers nearly the entire country east of the Mississippi as well as parts of Washington, Oregon, and California.
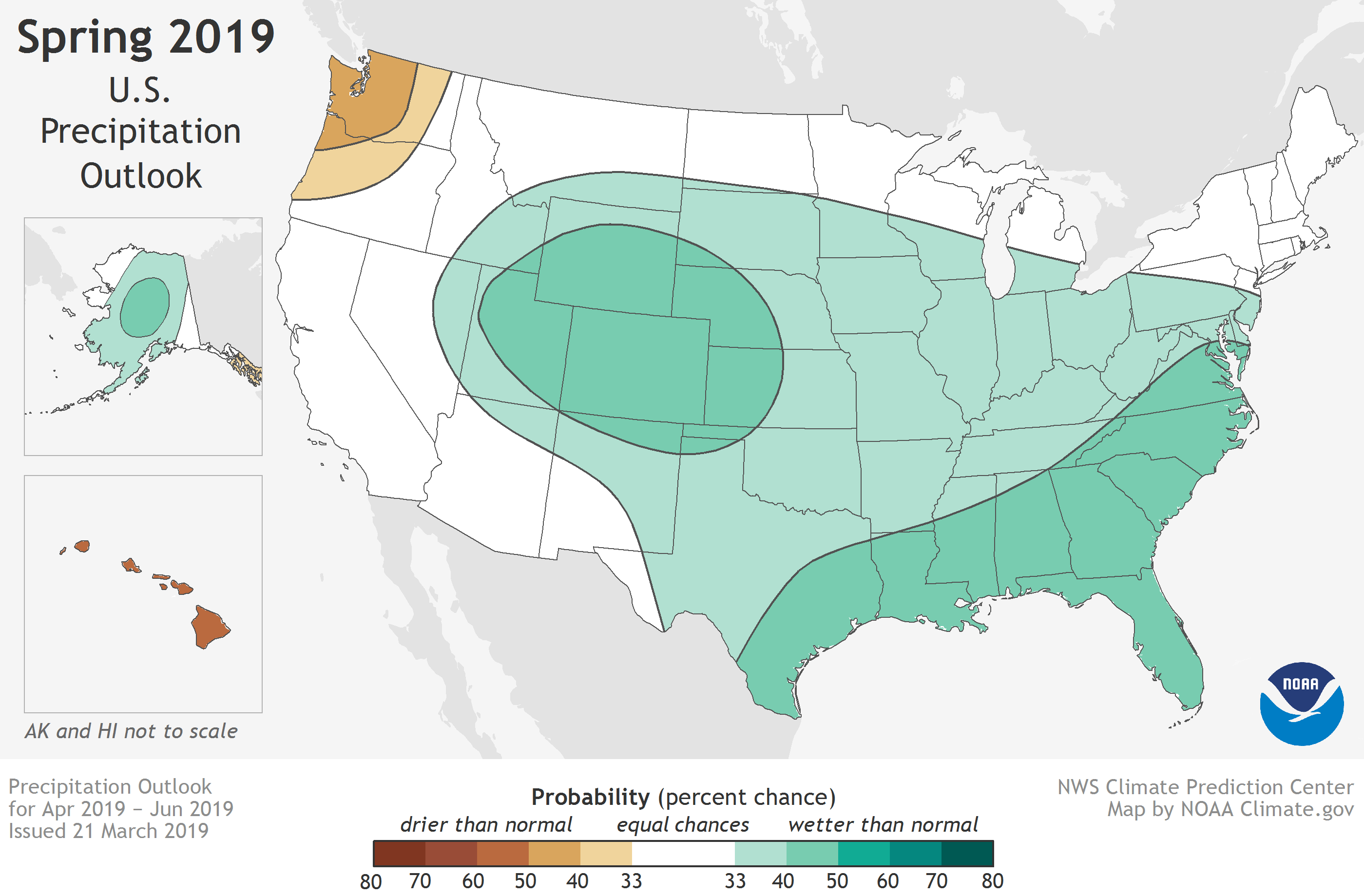
The wet winter isn’t the only contributor to the expansive flood risk. Across much of the country, the risk of well above average precipitation is elevated. (In any given year, the baseline probability for unusually wet, unusually dry, or near-average seasonal conditions is 33 percent each). For example, a swath of states along the southeastern seaboard and the Gulf Coast have a 40-50 percent chance of seasonal precipitation in the upper third of the climatological record. (That’s compared to a 33 percent chance of near-average precipitation and a 17-27 percent chance of precipitation in the lower third of the climatological record.)
Below-average temperatures are most likely in the Central and Southern Plains, where the saturated ground will slow down the seasonal warm up. Odds for a much warmer than average spring are elevated above background probability levels in Alaska (where lack of sea ice in surrounding waters allows more rapid seasonal warming), in areas east of the Mississippi, and in the West and Pacific Northwest.
For a more detailed discussion of the factors influencing this spring’s seasonal outlook, visit the Climate Prediction Center’s website. For experimental forecasts of departures from average stream flows, explore the interactive map on the Office of Water Prediction Website.
