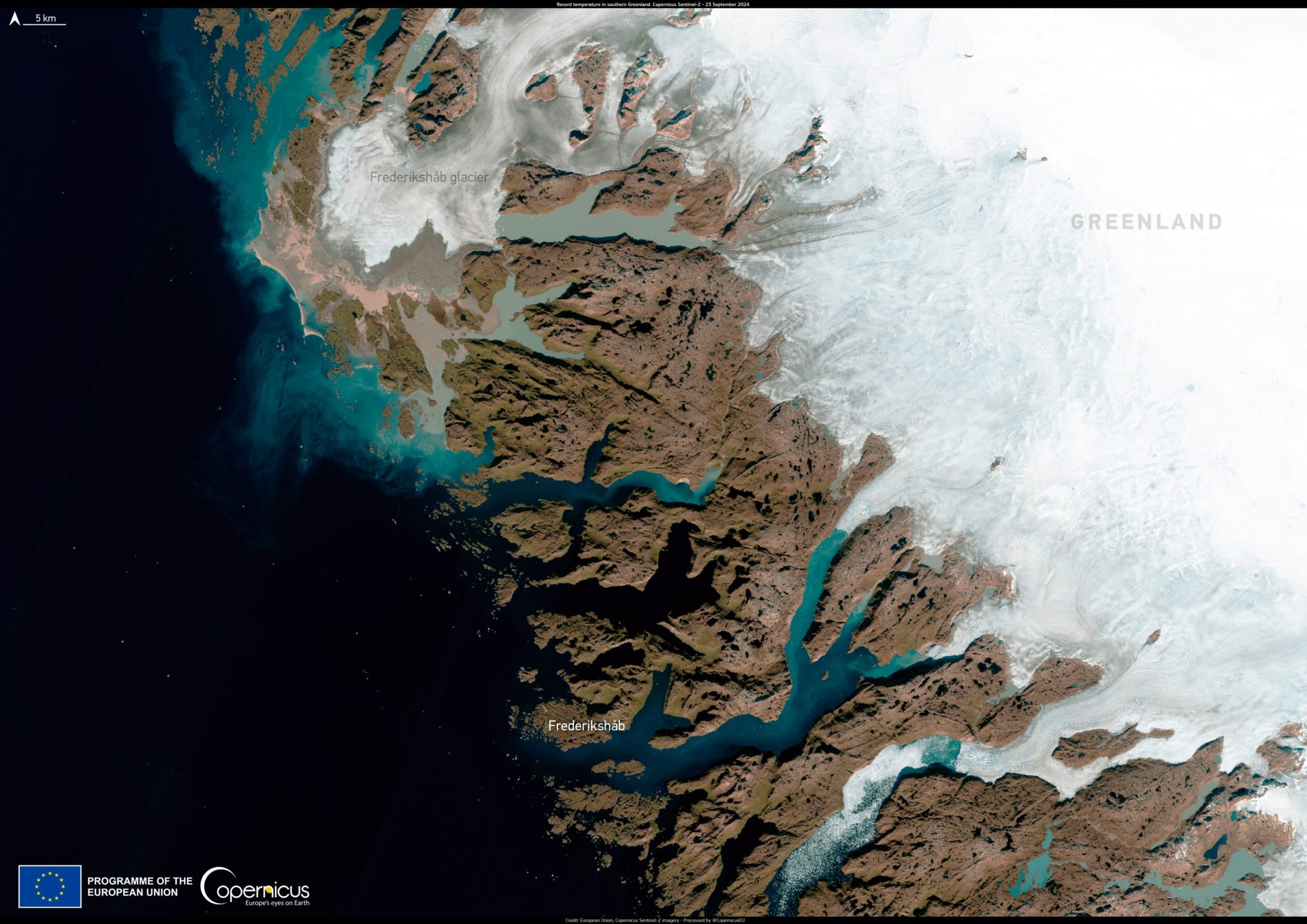
The town of Narsarsuaq in southern Greenland reached a record high night time temperature of 15.3°C (59.5°F) on September 22, the European Space Agency Copernicus reported. It marked the hottest September night in Narsarsuaq’s recorded history and one of the highest minimum temperatures ever recorded in all of Greenland. On average, nighttime temperatures for Narsarsuaq in September vary from 0.6°C (33°F) to 4.4°C (40°F), rarely falling below -2.8 27°F or exceeding 7.2°C (45°F).
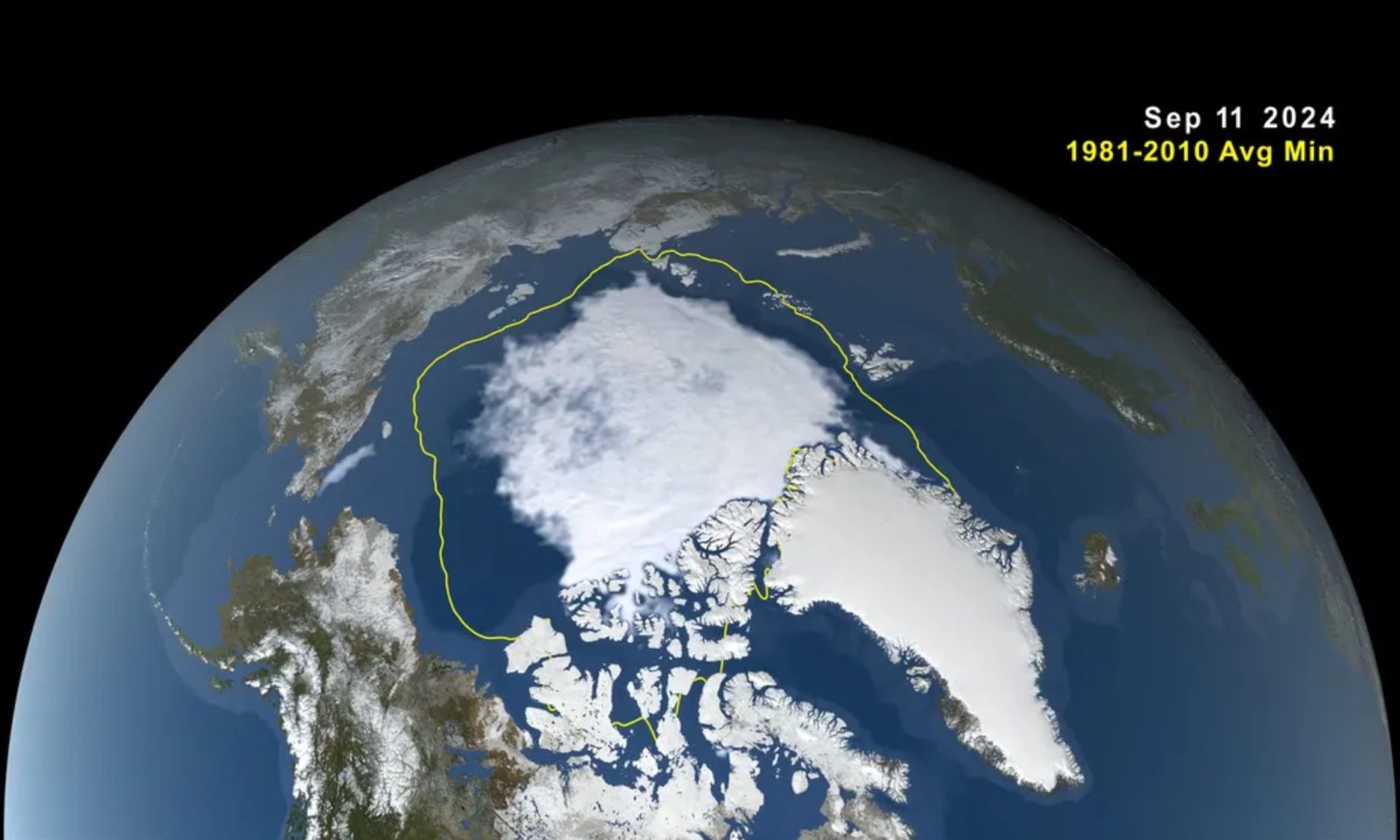
The Arctic has been warming at a rate above the global average and the Arctic ice has been shrinking at an alarming rate. The Arctic has been warming at between twice to four times the global average, a phenomenon known as ‘Arctic amplification.’ The amount of frozen seawater in the Arctic fluctuates during the year as the ice thaws and regrows from summer to winter. Data by NASA shows that over the last 46 years, the melting has been increasing while the new ice formation has been decreasing.
According to NASA, the Arctic ice shrank to 4.28 million square kilometers (1.65 million square miles). This is the seventh-lowest Arctic ice level since records began in the late 1970s. The lowest-ever level recorded was in September 2012, when the Arctic ice measured only 3.39 million square kilometers (1.31 million square miles).
The changes in the frozen water on Earth, known as the cryosphere, not only impact the Arctic ecosystem but also impact global weather patterns. The Arctic and Antarctic ice functions as our planet’s refrigerators. The white snow and ice reflect heat back into space, thereby balancing out other parts of the world that absorb heat, such as darker ocean surfaces. The reduction in Arctic and Antarctic ice impacts long-term climate patterns and causes more intense heat waves worldwide, shifts in precipitation patterns, and also more extreme winters as the polar jet stream is destabilized. In addition, the increasing decline of Arctic ice leads to rising sea levels as land-based ice is introduced into the oceans.
