The post first appeared on climate.gov and was written by Tom Di Liberto
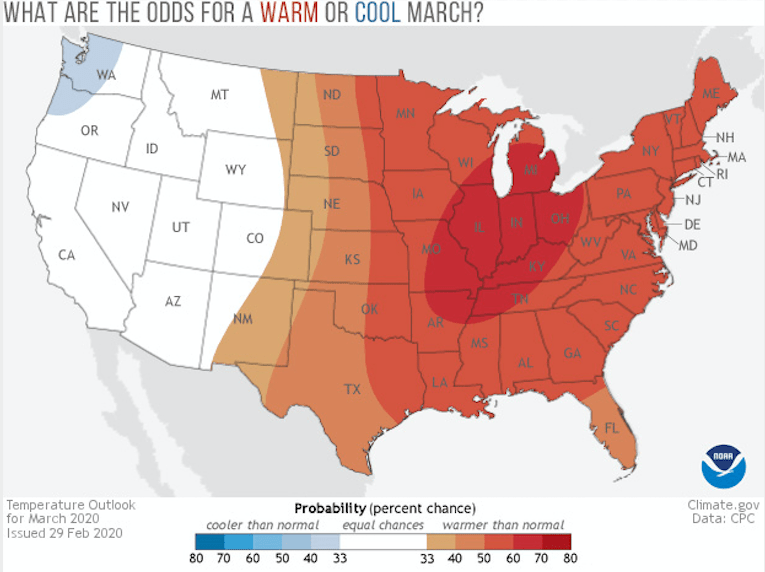
Welcome to meteorological spring! March kickstarts the transition season for many across the United States, and NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center has issued its monthly outlook for March 2020 temperature and precipitation. As a reminder, these outlooks don’t predict the actual numerical temperature or the exact amount of precipitation. Instead, they predict the probability that monthly temperatures and precipitation will be in the upper or lower third of the climatological record (defined as the 1981-2010 period) for a given location. Darker colors refer to a higher chance, not more extreme conditions.
The highest chance for above-average temperatures during March is located across the lower Mississippi Valley from northeastern Arkansas and western Tennessee to the lower Great Lakes in Michigan and southern Wisconsin. However, the entire central and eastern parts of the contiguous United States have a tilt in the odds toward above-average temperatures during March. Only the Pacific Northwest sees probabilities tilted towards a cooler-than-average March.
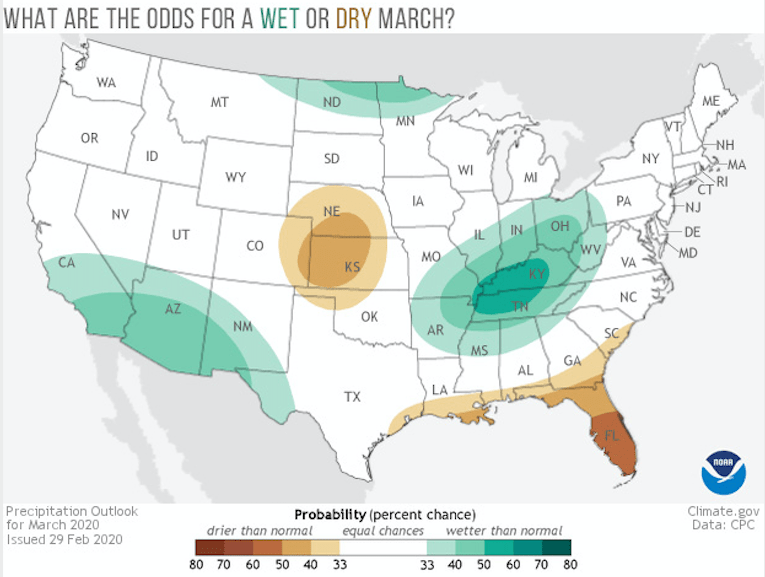
The increased chance for above-average temperatures in the Ohio Valley region coincides with an increased probability for a wetter March, with the highest odds in the Tennessee Valley. Another area where the odds are tilted toward a wetter March is along the US/Mexico border from southern California to western Texas. February in California was quite dry, so above-average rains would be helpful to the state’s reservoirs and ecosystems. On the flip side, March is favored to be dry for Florida and the Central Plains. For Alaska maps, visit the Climate Prediction Center’s webpage.
What about elsewhere?
The areas in white on the map refer to there being an equal chance (33.3%) that monthly temperature and precipitation will be above, below, or near average. Even odds occur when forecasters see no reason to expect one outcome over another at a given location. It doesn’t mean conditions are favored to be average.
What climate factors might give forecasters a reason to think a particular climate outcome is more likely? Phenomena like El Niño or La Niña, the Arctic Oscillation, or recent trends can influence monthly temperature and precipitation patterns. If these patterns give conflicting signals to forecasters or are judged to be too weak to influence climate patterns in a given location, forecasters might declare those areas to be “equal chances”. For March 2020, that includes much of the western United States for temperature, and much of the Great Plains, East Coast, Mountain West and Pacific Northwest for precipitation.
What was on the forecaster’s minds?
In their discussion of this month’s outlooks, the Climate Prediction Center noted that forecasts for the large-scale pattern suggest the influence of Pacific air across the continental United States. Across the far western United States, this means troughing bringing in cooler North Pacific air to the Pacific Northwest and farther south bringing moist air from the neighboring ocean to southern California, increasing the chance for a wetter than average March for southern California and cooler than average temperatures across the Pacific Northwest. Meanwhile across the central and eastern United States, winds out of the west and southwest will result in ridging or high pressure, meaning a better chance at warmer-than-average temperatures.
Forecasters also note that variability will be high, especially across the western United States, leading to the equal chance designation for temperatures across the West.
Join us on social media to let us know how your start to meteorological spring is going!