This article originally appeared on Climate.gov on August 8, 2023
Key Points:
- Heat waves impacted much of the U.S. in July and brought record temperatures to parts of the Southwest. The region as a whole tied with 2003 as the warmest July on record.
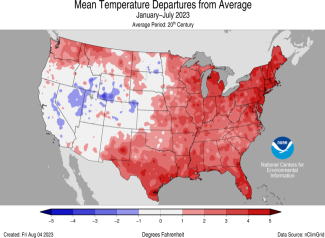
- Much of the eastern U.S. has been consistently warmer than average during 2023 with 28 states experiencing a top-10 warmest January–July including Florida, which ranked warmest on record.
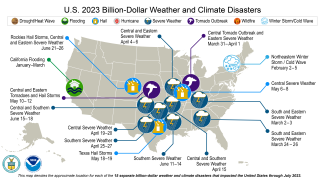
- A total of 15 billion-dollar weather and climate disasters have been confirmed this year—the most events since 1980 for the January-July period. These consisted of 13 severe storm events, one winter storm and one flooding event.
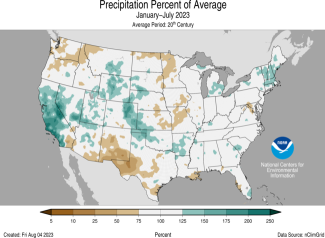
- This July was the 11th warmest on record for the nation, while precipitation ranked in the middle third of the historical record.
Other Highlights:
Temperature
July overnight temperatures were warmest on record across the New England region. The average temperature of the contiguous U.S. in July was 75.7°F, 2.1°F above average, ranking 11th warmest in the 129-year record. Generally, July temperatures were below average in the central and northern Plains and Upper Midwest. Temperatures were above average from the West Coast to the southern Plains and along the Gulf and East coasts and in parts of the Great Lakes. Arizona, New Mexico, Maine and Florida ranked warmest on record for July while Louisiana ranked second warmest on record. An additional 13 states ranked among their top-10 warmest July on record.
The Alaska statewide July temperature was 56.1°F, 3.4°F above the long-term average, ranking fifth warmest in the 99-year period of record for the state. Above-normal temperatures were observed across most of the state while pockets of near-average temperatures were observed in south central and southwestern portions of the state.
The Alaska January–July temperature was 27.6°F, 1.8°F above the long-term average, ranking in the warmest third of the historical record for the state. Much of the state was above normal for the seven-month period while temperatures were near average across much of the Interior and West Coast.
Precipitation
Across the state of Alaska, the average monthly precipitation was 3.51 inches, ranking in the middle third of the historical record. Conditions were wetter than average across most of the state while parts of the North Slope were near normal during the month. Below-normal precipitation was observed in parts of the Southeast Interior and Panhandle while parts of the Northeast Gulf had their driest July on record.
The January–July precipitation ranked 15th wettest in the 99-year record for Alaska, with above-average precipitation observed across much of the state. Near-normal precipitation was observed in parts of south-central Alaska, Southeast and in parts of the Aleutians during this period.
Billion-Dollar Disasters
There have been 15 confirmed weather and climate disaster events, each with losses exceeding $1 billion this year. These disasters consisted of 13 severe storm events, one winter storm and one flooding event. For this year-to-date period, the first seven months of 2023 rank highest for disaster count, ahead of 2017 with 14 disasters. The total cost of these events exceeds $39.7 billion, and they have resulted in 113 direct and indirect fatalities.
The U.S. has sustained 363 separate weather and climate disasters since 1980 where overall damages/costs reached or exceeded $1 billion (including CPI adjustment to 2023). The total cost of these 363 events exceeds $2.590 trillion.
Other Notable Events
A series of heat waves brought record-breaking temperatures to portions of the U.S. during July:
- July was the warmest month on record for Arizona and New Mexico by nearly 2°F.
- Across the Southwest, 36 counties each had their warmest July on record while an additional 63 counties ranked in the top-10 warmest for the month.
- Phoenix, Arizona had an average temperature of 102.8°F for the month of July—the hottest month on record for any U.S. city. Contributing to the record, Phoenix had 31 consecutive days of temperatures above 110°F from June 30 to July 30—breaking the previous record of 18 days set in 1974.
- On July 16, Death Valley soared to 128°F, setting a daily-temperature record, and reported its hottest midnight temperature on record at 120°F on July 17.
Several notable weather systems produced severe storms that impacted portions of the U.S. in July:
- On July 10, severe storms brought devastation and flooding to portions of the Northeast, as areas reported up to eight inches of rain within a 24-hour period. Montpelier, Vermont received a record-breaking 5.28 inches of rain, flooding the city and damaging thousands of homes and businesses.
- On July 18-19, a historic flash flood occurred over portions of Kentucky and Illinois after areas received rainfall totals up to 12 inches, causing significant damage and trapping residents in their homes. Mayfield, Kentucky received 11.28 inches of rain in a 24-hour period, likely breaking the state record for 24-hour rainfall.
- On July 24-25, an extreme thunderstorm outbreak produced more than 19,000 lightning strikes causing dozens of new wildfires in the state of Alaska. Overall, 2023 ranks as the second-lowest fire season, by acres burned, in the past 30 years for the state.
Drought
According to the August 1 U.S. Drought Monitor report, about 28.1% of the contiguous U.S. was in drought, up about 1.2% from the beginning of July. Moderate to exceptional drought was widespread across much of the Great Plains, with moderate to extreme drought in much of the Midwest and Florida Peninsula. Moderate to severe drought was present in parts of the Northwest, Southwest, southern Mississippi Valley, Mid-Atlantic, Michigan and Puerto Rico as well as moderate drought in parts of the Northeast and Alaska.
Drought conditions expanded or intensified along the Northern Tier, Upper Midwest, Southwest, southern Plains, Alaska and Puerto Rico during July. Drought contracted or was reduced in intensity across portions of the central Plains, Great Lakes, Ohio Valley, Northeast and in parts of the Great Basin.
Monthly Outlook
According to the July 31 One-Month Outlook from the Climate Prediction Center, much of the southern contiguous U.S., Pacific Northwest and Alaska favor above-normal monthly average temperatures in August, with the greatest odds along the Gulf Coast. The best chances for below-normal temperatures are forecast for the northern parts of the Rockies and Plains and in the Northeast. Much of the northern Rockies to the Mid-Atlantic and Northeast are favored to see above-normal monthly total precipitation whilebelow-normal precipitation is most likely to occur from eastern Arizona to the Florida Panhandle, as well as southwestern and southeastern Alaska.Drought improvement or removal is forecast from the central Plains to parts of the Great Lakes and in parts of the Mid-Atlantic, Florida and Puerto Rico, while persistence is more likely in portions of the Northwest, Southwest, southern Plains, northern Great Lakes and parts of the northern Plains and Hawaii. Drought development is likely in parts of the Northwest, Southwest, southern Plains and Hawaii.
According to the One-Month Outlook issued on August 1 from the National Interagency Fire Center, Hawaii and portions of the Northwest, Upper Midwest, Southwest, southern Plains, Lower Mississippi Valley, Southeast and eastern Alaska have above-normal significant wildland fire potential during August, while parts of California are expected to have below-normal potential for the month.
This monthly summary from NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information is part of the suite of climate services NOAA provides to government, business, academia and the public to support informed decision-making. For more detailed climate information, check out our comprehensive July 2023 U.S. Climate Report scheduled for release on August 11, 2023. For additional information on the statistics provided here, visit the Climate at a Glanceand National Maps webpages.