This post was written by Emily Becker for the NOAA ENSO Blog
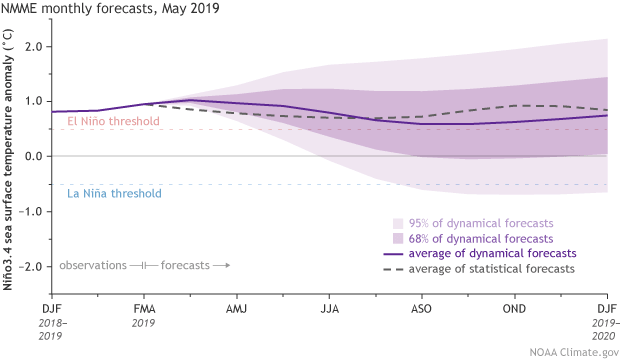
Forecasters estimate a 70% chance that our current El Niño will continue through the summer and a 55-60% chance it will extend into the fall.
Just a number
El Niño conditions were still evident across the tropical Pacific Ocean during April, as the sea surface temperature in the Niño3.4 region averaged about 0.7°C warmer than the long-term average (via the ERSSTv5 database). Most computer models predict that the ocean surface will stay warmer than average in the Niño3.4 region, with the majority of predictions remaining above the El Niño threshold of 0.5°C through next fall.
- The nerd’s version… NOAA El Niño Update: El Niño is Likely to Continue Through the Summer and Fall
However, there is a broad range of potential outcomes shown here, and we’re still within the spring predictability barrier, when forecast models have a tougher time making successful predictions, partly due to the tendency of ENSO to be in transition during the spring. We’re starting to pass that barrier, but we still bear it in mind when looking at forecasts made in early May.
Blow out your candles
The atmosphere also continued to reflect El Niño in April, with more clouds and rain forming over the warmer-than-average waters of the central tropical Pacific, and drier conditions over the far western Pacific and Indonesia, although this pattern was somewhat weaker than during February or March.
The near-surface winds in the tropical Pacific, the trade winds, were near average in April. The trade winds usually blow from the east to the west, keeping warm water piled up in the far western Pacific. Changes in these winds are a critical component of the El Niño system. When they weaken in the central Pacific, surface waters can warm, and sometimes allow a downwelling Kelvin wave to form: a large blob of warmer-than-average water that moves from the west to the east under the surface of the Pacific.
After a couple of months of weaker-than-average trade winds (what we expect during El Niño conditions), they were near average overall during April. This slight weakening of the typical El Niño signal is in part due to a reawakening Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) in the second half of April.
The MJO is an area of active storms and convection (rising air) that travels from west to east along the equator. It can circle the globe in about 30-60 days. We’ve talked about the MJO quite a bit on the ENSO Blog and climate.gov since this pattern can affect US weather, and interact with El Niño and La Niña.
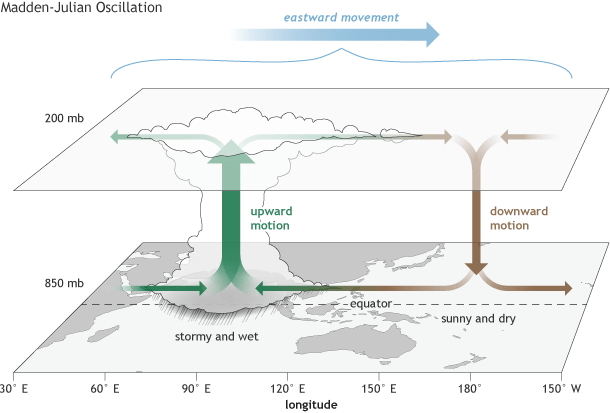
Near-surface air is drawn toward the MJO-related area of convection. So when the MJO is over the Indian Ocean, the trade winds in the west-central Pacific are stronger than average, because the inflow to the MJO reinforces them. But when the MJO moves into the central Pacific, the trade winds tend to be weaker, because the inflow to the MJO opposes them.
After going mostly quiet in mid-March, by mid-April the MJO was showing signs of re-development. The trade winds in the western Pacific during mid-late April were stronger than average (more east-to-west), consistent with what we’d expect when the center of MJO convection is in the Indian Ocean. However, during the first week of May, as the MJO moved into the Pacific, the trade winds weakened substantially in the west-central Pacific.
Over the hill
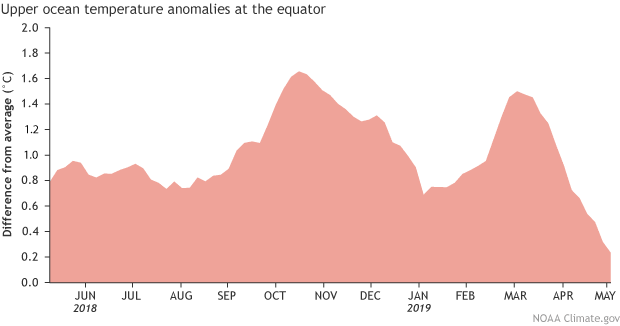
Over the past year, subsurface waters (from the surface down to about 1,000 feet) have remained warmer-than-average overall, but with some substantial increases and decreases, resembling a particularly brutal stage of the Tour de France. If the recent weakening in the trade winds does lead to a downwelling Kelvin wave and increases the subsurface anomalies, it could provide fuel to help this El Niño event to persist. Bikers beware, another uphill climb may be ahead of you.
Bon anniversaire
Lastly, happy 5th birthday to the ENSO Blog! We’ve learned a lot over the past 60 months, and we hope you have, too. We’ve reported on a slow-to-develop, but strong El Niño; consecutive weak La Niñas; and the current, weak El Niño. We’ve built an extensive catalog of posts on ENSO (the whole El Niño/La Niña system), other climate patterns, and many other climate-related topics. Check out our editor’s handy index page for a stroll down memory lane. And, never forget Tom’s three–post series on forecast verification.
The best part is that we have a long list of topics we’re looking forward to covering in future posts, and we’re happy to solicit suggestions in the comments section below on topics you would like us to cover. Thank you for reading us—we’ve had well over 2 million unique page views so far—otherwise, we’d just be yelling into the (trade) winds.